International Ice Hockey Federation: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
Previously, the IIHF also managed the development of inline hockey, however in June 2019 the IIHF announced that they would no longer govern inline hockey or organize the Inline Hockey World Championships. | Previously, the IIHF also managed the development of inline hockey, however in June 2019 the IIHF announced that they would no longer govern inline hockey or organize the Inline Hockey World Championships. | ||
==Presidents== | ==Presidents== | ||
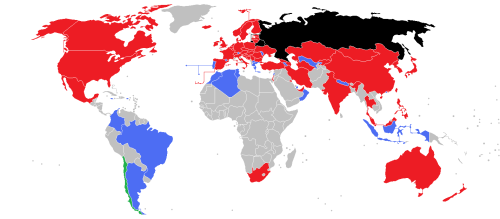
[[Image:IIHF Member Nations.png|thumb|500 px| | [[Image:IIHF Member Nations.png|thumb|500 px|Map of the world with current members of the IIHF. (<span style="color:red;">'''Red'''</span> indicates full members, <span style="color:blue;">'''blue'''</span> indicates associate members, <span style="color:green;">'''green'''</span> indicates affiliate members and <span style="color:black;">'''black'''</span> indicates suspended members.)]] | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- style="background:#e0e0e0;" | |- style="background:#e0e0e0;" | ||
| Line 186: | Line 186: | ||
[[File:IIHF Headquarters.jpg|thumb|250px|The IIHF's headquarters in Zurich.]] | [[File:IIHF Headquarters.jpg|thumb|250px|The IIHF's headquarters in Zurich.]] | ||
{{main|List of members of the International Ice Hockey Federation}} | {{main|List of members of the International Ice Hockey Federation}} | ||
As of | As of 2024, the IIHF has 82 members.<ref name="IIHFMemberStructure">{{cite web |url=https://www.iihf.com/en/associations |title=IIHF Member National Associations |date=29 September 2022 |publisher=International Ice Hockey Federation}}</ref> | ||
The federation has 60 full members, including two suspended members: [[Australia]], [[Austria]], [[Azerbaijan]], [[Belarus]] (suspended), [[Belgium]], [[Bosnia and Herzegovina]], [[Bulgaria]], [[Canada]], [[China]], [[Chinese Taipei]](Taiwan), [[Croatia]], [[Czech Republic|Czechia]], [[Denmark]], [[Estonia]], [[Finland]], [[France]], [[Georgia (country)|Georgia]], [[Germany]], [[United Kingdom|Great Britain]], [[Hong Kong]], [[Hungary]], [[Iceland]], [[India]], [[Iran]], [[Ireland]], [[Israel]], [[Italy]], [[Japan]], [[Kazakhstan]], [[North Korea]], [[South Korea]], [[Kuwait]], [[Kyrgyzstan]], [[Latvia]], [[Lithuania]], [[Luxembourg]], [[Malaysia]], [[Mexico]], [[Mongolia]], [[Netherlands]], [[New Zealand]], [[Norway]], the [[Philippines]], [[Poland]], [[Qatar]], [[Romania]], [[Russia]] (suspended), [[Serbia]], [[Slovakia]], [[Slovenia]], [[South Africa]], [[Spain]], [[Sweden]], [[Switzerland]], [[Thailand]], [[Turkey]], [[Turkmenistan]], [[Ukraine]], the [[United Arab Emirates]], and the [[United States]]. Full members have a national body dedicated to the sport, and participate annually in the international championships. Only full members have voting rights. | The federation has 60 full members, including two suspended members: [[Australia]], [[Austria]], [[Azerbaijan]], [[Belarus]] (suspended), [[Belgium]], [[Bosnia and Herzegovina]], [[Bulgaria]], [[Canada]], [[China]], [[Chinese Taipei]](Taiwan), [[Croatia]], [[Czech Republic|Czechia]], [[Denmark]], [[Estonia]], [[Finland]], [[France]], [[Georgia (country)|Georgia]], [[Germany]], [[United Kingdom|Great Britain]], [[Hong Kong]], [[Hungary]], [[Iceland]], [[India]], [[Iran]], [[Ireland]], [[Israel]], [[Italy]], [[Japan]], [[Kazakhstan]], [[North Korea]], [[South Korea]], [[Kuwait]], [[Kyrgyzstan]], [[Latvia]], [[Lithuania]], [[Luxembourg]], [[Malaysia]], [[Mexico]], [[Mongolia]], [[Netherlands]], [[New Zealand]], [[Norway]], the [[Philippines]], [[Poland]], [[Qatar]], [[Romania]], [[Russia]] (suspended), [[Serbia]], [[Slovakia]], [[Slovenia]], [[South Africa]], [[Spain]], [[Sweden]], [[Switzerland]], [[Thailand]], [[Turkey]], [[Turkmenistan]], [[Ukraine]], the [[United Arab Emirates]], and the [[United States]]. Full members have a national body dedicated to the sport, and participate annually in the international championships. Only full members have voting rights. | ||
In addition, there are 22 associate members who either do not have a national body dedicated to the sport, or do not regularly participate in the international championships. They are [[Algeria]], [[Andorra]], [[Argentina]], [[Armenia]], [[Brazil]], [[Colombia]], [[Greece]], [[Indonesia]], [[Jamaica]], [[Lebanon]], [[Liechtenstein]], [[Macau | In addition, there are 22 associate members who either do not have a national body dedicated to the sport, or do not regularly participate in the international championships. They are [[Algeria]], [[Andorra]], [[Argentina]], [[Armenia]], [[Brazil]], [[Colombia]], [[Greece]], [[Indonesia]], [[Jamaica]], [[Lebanon]], [[Liechtenstein]], [[Macau]], [[Morocco]], [[Nepal]], [[North Macedonia]], [[Oman]], [[Portugal]], [[Puerto Rico]], [[Singapore]], [[Tunisia]], and [[Uzbekistan]]. | ||
The IIHF recognizes [[Chile]] as an affiliated member that only participates in inline championships. | The IIHF recognizes [[Chile]] as an affiliated member that only participates in inline championships. | ||
| Line 240: | Line 240: | ||
{{IIHF members}} | {{IIHF members}} | ||
{{Wikipedia}} | {{Wikipedia}} | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Ice hockey governing bodies]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:41, 8 August 2024
The International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF; French: Fédération internationale de hockey sur glace; German: Internationale Eishockey-Föderation) is a worldwide governing body for ice hockey. It is based in Zurich, Switzerland, and has 83 member countries.
The IIHF maintains the IIHF World Ranking based on international ice hockey tournaments. Rules of play for IIHF events differ from hockey in North America and the rules of the National Hockey League (NHL). Decisions of the IIHF can be appealed through the Court of Arbitration for Sport in Lausanne, Switzerland. The IIHF maintains its own hall of fame for international ice hockey. The IIHF Hall of Fame was founded in 1997, and has been located within the Hockey Hall of Fame since 1998.
Previously, the IIHF also managed the development of inline hockey, however in June 2019 the IIHF announced that they would no longer govern inline hockey or organize the Inline Hockey World Championships.
Presidents
| Name | Years |
|---|---|
| 1908–1912 | |
| 1912–1914 | |
| 1914 | |
| 1914 | |
| 1914–1920 | |
| 1920–1922 | |
| 1922–1947 | |
| 1947–1948 | |
| 1948–1951 | |
| 1951–1954 | |
| 1954–1957 | |
| 1957–1960 | |
| 1960–1963 | |
| 1963–1966 | |
| 1966–1969 | |
| 1969–1975 | |
| 1975–1994 | |
| 1994–2021 | |
| 2021–present |
Functions
The main functions of the IIHF are to govern, develop and organize hockey throughout the world. Another duty is to promote friendly relations among the member national associations and to operate in an organized manner for the good order of the sport. The federation may take the necessary measures in order to conduct itself and its affairs in accordance with its statutes, bylaws and regulations as well as in holding a clear jurisdiction with regards to ice hockey at the international level. The IIHF is the body responsible with arranging the sponsorships, license rights, advertising and merchandising in connection with all IIHF competitions.
Another purpose of the federation is to provide aid in the young players' development and in the development of coaches and game officials. On the other hand, all the events of IIHF are organized by the federation along with establishing and maintaining contact with any other sport federations or sport groups. The IIHF is responsible for processing the international players' transfers. It is also the body that presides over ice hockey at the Olympic Games as well as over all levels of the IIHF World Championships. The federation works in collaboration with local committees when organizing its 25 World Championships, at five different categories.
Even though the IIHF runs the world championships, it is also responsible for the organization of several European club competitions such as the Champions Hockey League or the Continental Cup.
The federation is governed by the legislative body of the IIHF which is the General Congress along with the executive body, which is the Council. The Congress is entitled to make decisions with regard to the game's rules, the statutes and bylaws in the name of the federation. It is also the body that elects the president and the council or otherwise known as board.[5] The president of the IIHF is basically the representative of the federation. He represents the federation's interests in all external matters and he is also responsible that the decisions are made according to the federation's statutes and regulations. The president is assisted by the General Secretary, who is also the highest ranked employee of the IIHF.
History
1908–1913
The International Ice Hockey Federation was founded on May 15, 1908 at 34 Rue de Provence in Paris, France, as Ligue International de Hockey sur Glace (LIHG).[1] The founders of the federation were representatives from Belgium, France, Great Britain, Switzerland and Bohemia (now Czech republic). Louis Magnus, the French representative, was the fifth member to sign the founding document and also the first president of the LIHG.
The second congress was held from January 22-25, 1909 in Chamonix, France. Playing and competitions rules were established, and an agreement was reached for an annual European Championship to be contested, beginning in 1910. The 1909 Coupe de Chamonix was contested during the congress. It was won by Princes Ice Hockey Club, representing Great Britain. Germany became the sixth LIHG member on September 19, 1909.[2]
The third LIHG Congress was held on January 9, 1910 in Montreux, Switzerland. Louis Magnus was re-elected president and Peter Patton took on the position of vice-president. The first European Championship began in Les Avants a day after the conclusion of the congress. It was won by Great Britain.[2]
Russia was added as the seventh LIHG member and Herman Kleeberg replaced Peter Patton as vice president at the fourth LIHG Congress, which was held in Berlin from February 16-17, 1911, in conjunction with the 1911 European Championship.[2]
The fifth LIHG Congress took place from March 22-23, 1912, in Brussels, Belgium. Unlike the two previous conferences, it was not held in conjunction with the European Championships, which had been staged in Prague in early February. A verdict was reached regarding the fate of the past month's European Championship, which had been the subject of a protest by Germany. It was decided that the tournament would be annulled as Austria was not yet an LIHG member at the time of its playing. Austria, along with Sweden and Luxembourg, were accepted as LIHG members at the congress. Henri Van den Bulcke succeeded Louis Magnus as LIHG president, and Max Sillig replaced Herman Kleeberg as vice-president. The first LIHG Championship was contested in Brussels from March 20-24. It was held annually until 1914.[2]
At the 1913 congress in St. Moritz, Max Sillig resigned his position as vice-president and was replaced by Peter Patton, who had previously served in the position from 1910-1911.[2]
1914–1945
The 1914 congress was held in Berlin, the location of that year's European Championship. Louis Magnus replaced Van den Bulcke as president, but he resigned immediately as the other delegates did not follow his program. Peter Patton, vice-president at the time, then became president and had new elections staged. Van den Bulcke was again elected as president (a position he would hold until 1920), and Patton was returned to his prior role of vice-president.[3]
World War I interrupted all activities of the federation between 1914 and 1920. The LIHG expelled Austria and Germany from its ranks following the war in 1920. Bohemia's membership was transferred to the new country of Czechoslovakia the same year.[3]
The 1920 Olympics were the first to integrate hockey into their program. Canada and the United States made their debut on the international scene at the tournament. Their level of play was vastly superior to that of the Europeans and Canada took home the gold while the US won the silver medal. On 26 April 1920, at the LIHG Congress which was held during the Olympic tournament, both countries became members of the federation. Also at the congress, Max Sillig became president, and Paul Loicq and Frank Fellowes were elected as vice presidents.[3]
Paul Loicq was elected as president in 1922. Dr. Karel Hartmann and Haddock were chosen as the new vice-presidents.[3]
At the 1923 congress it was decided to consider the 1924 Olympic Games as the World Championship as well as to organize a parallel European Championship. Romania, Spain, and Italy were admitted to the LIHG the same year.[3]
Austria was re-admitted to the LIHG in 1924, while the Swedish proposal to re-admit Germany was declined. The Swedes protested by leaving the LIHG. They returned in 1926 following the re-admission of Germany.[3]
The 1928 Winter Olympics, which also served as the World and European Championship for the year, saw a record 11 countries participate as Canada claimed their third gold medal.[3]
At the 1929 congress, the LIHG decided to organize a stand-alone World Championship, beginning in 1930. The first World Championship began in Chamonix, but had to be concluded in Vienna and Berlin as the natural ice in Chamonix melted toward the end of the tournament. Canada was considered so dominant that it received a bye to the final, where it easily dispatched Germany to win the gold medal. Japan, which had joined the LIHG just days prior to the start of the tournament, entered a team consisting of medical students.[3]
The 1932 Winter Olympics, held in Lake Placid, consisted of only four teams due to the global financial crisis. Germany and Poland were the only European nations present as Canada won their fourth Olympic gold medal. The 1932 European Championship was contested as the last stand-alone European Championship. Nine countries participated and Sweden won their third European title.[3]
The LIHG celebrated its 25th anniversary in 1933. Since its foundation in 1908, 18 European Championships, six World Championships, and four Olympic Games tournaments had been contested. The 1933 World Championship marked the first time that Canada failed to emerge victorious in a World Championship or Olympic tournament. They were defeated by the United States, 2-1 in overtime.[3]
The Netherlands and Norway became LIHG members in 1935. The three Baltic states, Latvia, Estonia, and Lithuania joined the LIHG in 1931, 1935, and 1938 respectively. South Africa was accepted into the LIHG in 1937.[4]
The 1936 Winter Olympics set a new record with 15 participants. Great Britain, consisting of a team in which nine of the 13 players had grown up in Canada, won their first and only Olympic gold medal at the tournament.[4]
World War II disrupted all LIHG events - World, European, and Olympic tournaments alike - spanning from 1940 to 1946.[4]
1946–1956
The first LIHG Congress in seven years was held in Brussels on April 27, 1946. Germany and Japan were expelled from the federation, while the memberships of the three Baltic states - Estonia, Latvia, and Estonia - were voided due to their annexation by the Soviet Union. Austria had its membership restored. It had been voided in 1939 following the country's union with Germany. Denmark entered the LIHG as a new member.[5]
The first World Championship following the war was held in Prague in February 1947. Despite Canada's absence from the tournament, it received great fan support (especially from the Czechoslovak fans) as Czechoslovakia captured the gold medal. Paul Loicq, who had been the LIHG president for 25 years, resigned his position at the LIHG Congress which was being held simultaneously with the World Championship. He was replaced by Dr. Fritz Kraatz.[5]
The 1948 Winter Olympics in St. Moritz were the subject of a power struggle between two American federations, the Amateur Athletic Union (AAU; recognized by the International Olympic Committee), and the Amateur Hockey Association (AHA; recognized by the LIHG), both of which had sent teams to the tournament. The IOC initially declared that neither team would be allowed to participate, which led the LIHG to threaten a boycott of the entire ice hockey tournament. The IOC then conceded and allowed the AHA team to participate in the tournament and the AAU team to march in the opening ceremony. The AHA team was excluded from the final rankings of the Olympic tournament, but not from the World Championship, where they officially finished in fourth place.[5]
George Hardy replaced Fritz Kraatz as president in 1948. He would hold the position for three years, before being replaced by Kraatz, who began his second term in office as LIHG president. Germany and Japan were re-admitted and the Soviet Union - which would go on to win their first World Championship during their inaugural appearance in 1954 - joined as a new member during his tenure.[5]
Walter A. Brown was elected LIHG president in 1954, replacing Dr. Fritz Kraatz. Meanwhile, the federation adopted an English name and became the International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF). East Germany became the IIHF's 25th member in 1956.[6]
1957–1974
The Hungarian Revolution of 1956 which had caused Hungary to be occupied by the Soviet Army, led to a boycott of the 1957 World Championships, which were being staged in Moscow. Canada and the United States led the boycott, and were joined by Norway, West Germany, Italy, and Switzerland.[6]
The IIHF welcomed several new members between 1960 and 1963. Bulgaria and North Korea joined in 1960 while China and South Korea were accepted into the federation in 1963.[6]
At the 1961 World Championship in Switzerland, the West German team - as advised by their federal government - refused to compete against East Germany, as in the event of an East German victory, they would've had to pay respects to the East German flag. The game was awarded to East Germany, 5-0, by virtue of a forfeit. Two years later, at the 1963 World Championship in Stockholm, the East Germans took payback on West Germany. Following a 4-3 defeat to the West Germans, the East German players turned their backs in unison to the West German flag as it was being hoisted.[6]
The 1962 World Championship, hosted by the American cities of Colorado Springs and Denver, was boycotted by the Soviet Union and Czechoslovakia, which led to a further boycott by the other Eastern Bloc countries. At issue was the boycott of the 1957 championships in Moscow by Canada and the USA, and the Americans refusal of East German passports in reaction to the building of the Berlin Wall.[6]
The lower pools (A, B, and C) were contested annually beginning in 1961 and promotion-and-relegation between the pools started the same year. While the B Pool had been played as early as 1951, it was not held every year due to a frequent shortage of teams, and no promotion-and-relegation took place between it and the top division.[6]
For the 1965-66 season, the IIHF created the European Cup, a tournament consisting of the top club teams from around Europe. The competition was originated by Günther Sabetzki, based on the association football European Cup (now UEFA Champions League). In 1968 the IIHF organized the European U19 Championship, a junior competition for players aged 19 and under. The age limit was later reduced to 18 in 1977.[6]
The IIHF saw three different presidents take office between 1957 and 1974. John F. "Bunny" Ahearne was elected to three separate terms (the first from 1957-1960, the second from 1963-1966, and the third spanning from 1969-1975). The Canadian Robert Lebel served in office from 1960-1963, while William Thayer Tutt of the United States was president from 1966-1969.[6]
1975–1989
In 1975, Dr. Günther Sabetzki was elected president of the IIHF. He replaced Bunny Ahearne, whose heavy-handed regime had caused him to grow increasingly unpopular toward the end of his presidency. Sabetzki would remain in office for nearly two decades, which were considered up to that point the most successful period for international ice hockey on all fronts.[7]
Sabetzki's greatest achievement was ending the Canadian boycott of the World Championships and Olympic Games. The Canadians had boycotted these tournaments between 1970 and 1976 after the IIHF had refused to allow them to roster professional players at the World Championships from NHL teams that had not qualified for the Stanley Cup playoffs. President Sabetzki managed to find a compromise that resulted in the return of Canada to international events beginning in 1977. The pro players whose teams had been eliminated from the playoffs were allowed to compete and in exchange, Canada and the U.S. agreed to participate in the World Championships. They also waived their right to host any World Championships. The creation of the Canada Cup (a competition organized by the NHL in Canada every four years) was also part of the new agreement between the IIHF and North American professional hockey.[7]
The first official World Junior Championship for players aged 20 and under was held in 1977. Unofficial tournaments, which were not IIHF-sanctioned and teams were eligible to participate by invitation only, had been contested between 1974 and 1976. It began as a relatively obscure tournament, but soon grew in popularity, particularly in Canada. The most infamous WJC event was the Punch-up in Piestany in 1987, where a bench-clearing brawl between Canada and the Soviet Union resulted in the expulsion of both countries from the tournament.[8]
Two new tournaments were introduced by the IIHF during the 1980s. The IIHF Asian Oceanic U18 Championship, which was held annually until 2002, was played for the first time in 1984. The first Women's European Championship was contested in 1989. It would be held a total of five times between 1989 and 1996.[9]
1990–present
The IIHF continued to grow in numbers during the 1980s and 1990s, both due to political events and the continued growth of hockey worldwide. The dissolution of the Soviet Union saw its membership transferred to Russia, and the addition of four ex-Soviet republics; Azerbaijan, Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Ukraine to the federation. In addition, the memberships of Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania - all of which had initially joined the IIHF in the 1930s but were expelled following their annexation by the Soviet Union - were renewed. The breakup of Yugoslavia also resulted in an increase in membership. Croatia and Slovenia joined as new members, while the membership of the old Yugoslavia was transferred to FR Yugoslavia (which later became known as Serbia and Montenegro and still later dissolved into the independent republics of Serbia and Montenegro). When Czechoslovakia broke up, its membership rights were transferred to the Czech Republic and Slovakia was admitted as a new member. The influx of new members resulted in the IIHF increasing the size of the Group A tournament. It expanded from 8 teams to 12 in 1992 and from 12 to 16 in 1998.[10]
The other new members to join the IIHF during the 1980s and 1990s were: Chinese Taipei (1983), Hong Kong (1983), Brazil (1984), Mexico (1985), Kuwait (1985), Greece (1987), India (1989), Thailand (1989), Israel (1991), Turkey (1991), Iceland (1992), Andorra (1995), Ireland (1996), Singapore (1996), Argentina (1998), Namibia (1998), Armenia (1999), Chile (1999), Mongolia (1999), and Portugal (1999).[10]
In June 1994, René Fasel was elected the President of the IIHF, succeeding Günther Sabetzki. He has served five consecutive terms as president. His most recent started in 2012 after he was re-elected at the IIHF General Congress in Tokyo, Japan. In March 1995, he helped negotiate an agreement so that NHL players could compete at the 1998 Winter Olympics in Nagano, Japan.[11]
The first Women's World Championship was contested in 1990 in the Canadian capital of Ottawa. Canada and the United States have dominated the event, winning all 15 tournaments (10 by the Canadians and five by the U.S.) since its inception. The 1998 Winter Olympics were the first to feature women's ice hockey as part of its program.[8]
Numerous other tournaments have been created by the IIHF during the 1990s and 2000s. The IIHF World U18 Championships (1999), IIHF Women's Pacific Rim Championships (played in 1995 and 1996), IIHF Continental Cup (1997; known as the IIHF Federation Cup from 1994-1996), European Hockey League (contested from 1996-2000) and the IIHF Super Cup (contested from 1997-2000) were introduced during the 90s. The Euro Ice Hockey Challenge (2001), IIHF European Women's Champions Cup (2004), Elite Women's Hockey League (2004), IIHF European Champions Cup (contested from 2005-2008), IIHF World Women's U18 Championships (2008), Victoria Cup (played in 2008 and 2009), Champions Hockey League (operated during the 2008-09 season), and the IIHF Challenge Cup of Asia (2008) all were created during the 2000s.[8]
The IIHF celebrated its 100th anniversary in 2008. As part of the celebrations, the 2008 World Championship was held in Canada for the first time (the tournament was co-hosted by the cities of Halifax and Quebec City).[8]
The number of members continued to grow in the 21st century: Chile (2000), Bosnia and Herzegovina (2001), Liechtenstein (2001), North Macedonia (2001), the United Arab Emirates (2001), Macau (2005), Malaysia (2006), Moldova (2008), Georgia (2009), Kuwait (2009; had originally joined in 1985, but was expelled in 1992), Morocco (2010), Kyrgyzstan (2011), Jamaica (2012), Qatar (2012), Oman (2014), Turkmenistan (2015), Indonesia (2016), Nepal (2016), the Philippines (2016), Algeria (2019), Colombia (2019), Iran (2019), Lebanon (2019), Uzbekistan (2019), and Tunisia (2021)..[10]
Namibia, which was an affiliate member of the IIHF until 2017, withdrew from an IIHF membership and was removed entirely due to lack of ice hockey activities in the country. Namibia still maintain to play in-line hockey and as a member of World Skate since the dissolution of the International Roller Sports Federation (FIRS) and the merger with the International Skateboarding Federation in September 2017.[10]
The IIHF received international criticism for holding the 2014 Men's Ice Hockey World Championships in Belarus because of the poor human rights record of the country. Several human rights organisations launched the "Don't play with the dictator!" boycott campaign and there were appeals from the US Congress, German Parliament and the European Parliament. The IIHF again received criticism for planning to partly hold the 2021 Men's Ice Hockey World Championships in Belarus. In January 2021, the IIHF withdrew the 2021 World Championship from Minsk due to safety and security issues during the political unrest, besides the COVID-19 pandemic and decided to solely hold the tournament in Riga, Latvia.
On May 23, 2021 civilian Ryanair Flight 4978, which was enroute from Athens to Vilnius, was forced to land in Minsk and a passenger of that flight was detained. In protest, Latvian officials replaced the Belarusian state flag in Riga with the former flag associated with the Belarusian opposition groups, including at the 2021 IIHF World Championship display of flags. This was by order of Mayor of Riga Mārtiņš Staķis and Minister of Foreign Affairs of Latvia Edgars Rinkēvičs. The IIHF issued a statement protesting the replacement of the flag, and IIHF president René Fasel asked the mayor to remove the IIHF name, its flag and its symbols from such sites, or to restore the flag, insisting that the IIHF is an "apolitical sports organization". In response, Staķis said he would remove the IIHF flags.
On 28 February 28 2022, the IIHF suspended the memberships of the Russian and Belarusian hockey federations until further notice due to the countries' invasion of Ukraine. Still, non-Russian players in Russian clubs are according to IIHF rules bound by their contracts, and can not leave their clubs and Russia until their contracts expire or is terminated by their club. If players leave anyway they can be sued and would be blocked from playing for other clubs.
On 22 March 2023, the IIHF excluded Russian and Belarusian national and club teams from IIHF competitions during the 2023–24 season, based on safety considerations.
Members
As of 2024, the IIHF has 82 members.[12]
The federation has 60 full members, including two suspended members: Australia, Austria, Azerbaijan, Belarus (suspended), Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Canada, China, Chinese Taipei(Taiwan), Croatia, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Georgia, Germany, Great Britain, Hong Kong, Hungary, Iceland, India, Iran, Ireland, Israel, Italy, Japan, Kazakhstan, North Korea, South Korea, Kuwait, Kyrgyzstan, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malaysia, Mexico, Mongolia, Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, the Philippines, Poland, Qatar, Romania, Russia (suspended), Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, South Africa, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Thailand, Turkey, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, the United Arab Emirates, and the United States. Full members have a national body dedicated to the sport, and participate annually in the international championships. Only full members have voting rights.
In addition, there are 22 associate members who either do not have a national body dedicated to the sport, or do not regularly participate in the international championships. They are Algeria, Andorra, Argentina, Armenia, Brazil, Colombia, Greece, Indonesia, Jamaica, Lebanon, Liechtenstein, Macau, Morocco, Nepal, North Macedonia, Oman, Portugal, Puerto Rico, Singapore, Tunisia, and Uzbekistan.
The IIHF recognizes Chile as an affiliated member that only participates in inline championships.
IIHF Hall of Fame
- Main article: IIHF Hall of Fame
Prior to the establishment of the IIHF Hall of Fame, the IIHF displayed a collection of historical artifacts from World Championships and the Olympic Games in temporary exhibits. From 1992 to 1997, the IIHF loaned its exhibits to the International Hockey Hall of Fame in Kingston, Ontario.[13]
The first step taken by the IIHF to create its own hall of fame was a proposal made in 1996, which was later ratified at the 1997 IIHF summer congress to host the museum in Zürich.[13] The approval came exactly 89 years from the foundation of the IIHF, with the purpose of honoring former international ice hockey players, builders (administrators) and officials.[14] The annual induction ceremony takes place on the medal presentation day of the Ice Hockey World Championships.[13][14] The IIHF agreed with the National Hockey League to transfer its exhibits to the Hockey Hall of Fame in Toronto, as of 29 July 1998.[13]
Tournaments
National teams
- Ice Hockey World Championships
- IIHF World U20 Championship
- IIHF World U18 Championship
- IIHF World Women's Championships
- IIHF World Women's U18 Championships
Clubs
- Defunct
- IIHF European Cup
- European Hockey League
- IIHF European Champions Cup
- Champions Hockey League (2008–09)
- IIHF Super Cup
- IIHF Inline Hockey World Championship
Other national team tournaments
- NHL participation
- Ice hockey at the Olympic Games (1998–2014)
- Canada Cup–An NHL-sanctioned tournament played between professional players from the top teams in the world five times between 1976 and 1991.[15]
- World Cup of Hockey–The successor to the Canada Cup, played in 1996, 2004 and 2016.[15][16]
- Summit Series–The series played between Canada and the Soviet Union in 1972.[17]
- Other
- Ice Hockey European Championships–An annual ice hockey tournament for European countries associated to the International Ice Hockey Federation played from 1910 to 1991.
Chief Medical Officers
References
- ↑ IIHF and Paris International Ice Hockey Federation. Retrieved on 2010-02-18
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 IIHF 1908-1913
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 3.9 IIHF 1914-1933
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 IIHF 1934-1945
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 IIHF 1946-1956
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 IIHF 1957-1974
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 IIHF 1975-1989
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 IIHF Timeline
- ↑ Müller, Stephan (2005). International Ice Hockey Encyclopaedia 1904–2005. Germany: Books on Demand. ISBN 3-8334-4189-5.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 IIHF 1990-today
- ↑ IIHF Council
- ↑ "IIHF Member National Associations". International Ice Hockey Federation. 29 September 2022. https://www.iihf.com/en/associations.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 13.3 "IIHF Hall of Fame" (in ru). http://hockeyarchives.ru/iihf/hall_of_fame.html.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 "IIHF Hall of Fame". http://webarchive.iihf.com/iihf-home/history/the-iihf/iihf-hall-of-fame.html.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Burnside, Scott (2004-08-31). "World Cup is hockey at its best". ESPN. http://sports.espn.go.com/nhl/worldcup04/columns/story?id=1871031. Retrieved 2009-03-11.
- ↑ "NHL announces World Cup of Hockey for 2016". The Canadian Press. 2015-01-24. http://www.cbc.ca/sports/hockey/nhl/nhl-announces-world-cup-of-hockey-for-2016-1.2930670/. Retrieved January 31, 2015.
- ↑ "Summit Series '72 Summary". Legends of Hockey. Hockey Hall of Fame. Archived from the original on 2008-08-07. https://web.archive.org/web/20080807130920/http://www.hhof.com/html/GamesSummarySUM1972.shtml. Retrieved 2009-03-11.
- ↑ "Wolf-Dieter Montag – Curriculum Vitae" (in de). 19 November 2014. p. 2. http://www.gots.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/12/CV_Montag.pdf.
- ↑ "Paul Loicq Award: Dr Mark Aubry (CAN)". 2014. http://www.iihf.com/home-of-hockey/news/iihf-hof-2014/.
- ↑ "Dr. Mark Aubry – 2006 Dr. Tom Pashby Sports Safety Award". November 18, 2006. http://www.drpashby.ca/2006/11/dr-mark-aubry-2006-dr-tom-pashby-sports-safety-award.
| This page uses Creative Commons Licensed content from Wikipedia (view authors). |